(15 Credits/Hours)
Launch Date: August 5, 2025
Expires: August 31, 2027
Course Overview
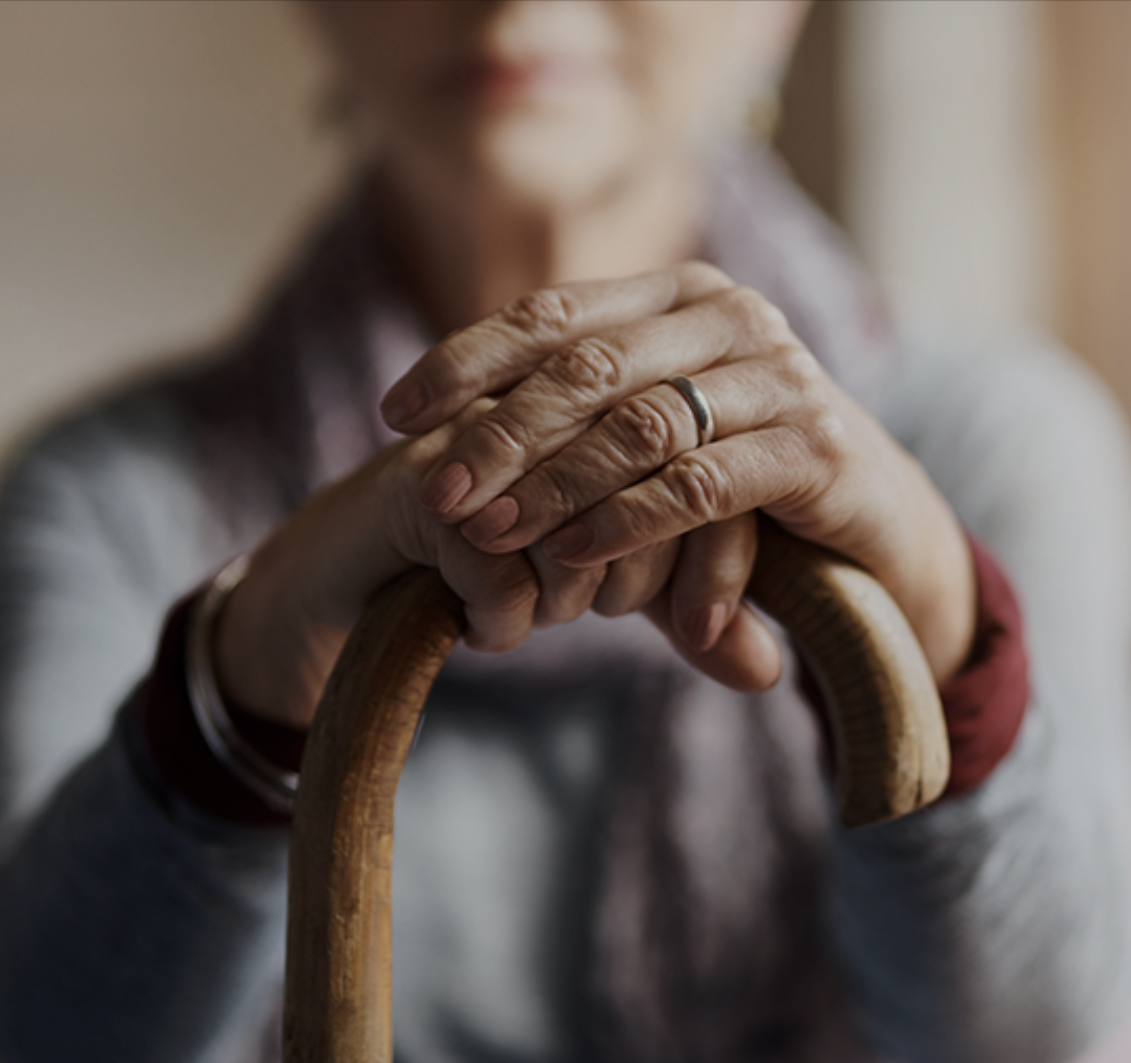
Falls represent one of the most significant patient safety challenges in healthcare settings today, affecting hundreds of thousands of hospitalized patients annually and resulting in serious injuries, extended hospital stays, and increased healthcare costs. This comprehensive continuing education course provides nurses with the essential knowledge and evidence-based strategies needed to effectively prevent patient falls and improve overall patient safety outcomes.
With over 700,000 to 1 million people falling in U.S. hospitals each year and approximately 25% of these falls resulting in injury, fall prevention has become a critical component of quality nursing care. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services’ decision to no longer reimburse hospitals for certain fall-related injuries has elevated fall prevention from a quality initiative to a financial imperative. More importantly, preventing falls directly impacts patient well-being, preserving dignity, independence, and quality of life.
This course synthesizes the latest research from leading healthcare organizations including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), National Institute on Aging (NIA), and The Joint Commission. You’ll gain practical skills in risk assessment, evidence-based intervention strategies, and interdisciplinary collaboration while understanding the regulatory and quality improvement frameworks that guide fall prevention programs.
Rather than presenting generic fall prevention strategies, this course emphasizes individualized, patient-centered care based on specific risk factors and evidence-based interventions. You’ll learn to move beyond simple risk scoring to implement comprehensive, multifactorial approaches that address the complex interplay of patient, environmental, and system factors that contribute to falls.
Learning Objectives
Upon completing this course, you will be able to:
- Analyze the scope and impact of falls in healthcare settings, including national statistics, economic costs, and patient outcomes
- Differentiate between types of falls (anticipated physiological, unanticipated physiological, and accidental) and their underlying causes
- Identify intrinsic and extrinsic risk factors that contribute to patient falls, including medication effects, environmental hazards, and patient-specific variables
- Compare evidence-based fall risk assessment tools including the Morse Fall Scale, Hendrich II Fall Risk Model, and STRATIFY, including their validation, strengths, and limitations
- Explain the regulatory framework surrounding fall prevention, including Joint Commission requirements, CMS reimbursement policies, and AHRQ guidelines
- Conduct comprehensive fall risk assessments using validated tools and clinical judgment to determine individual patient risk levels
- Implement evidence-based prevention interventions appropriate to specific risk factors, including universal precautions and targeted strategies
- Design individualized fall prevention care plans that address patient-specific risk factors and incorporate multifactorial intervention approaches
- Modify environmental factors to reduce fall risk, including room setup, lighting, equipment placement, and assistive device selection
- Integrate technology solutions appropriately, understanding the evidence base and limitations of alarm systems, monitoring devices, and smart room technologies
- Educate patients and families about fall prevention strategies using health literacy principles, cultural competency, and teach-back methodology
- Collaborate effectively with interdisciplinary team members including physicians, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and pharmacists in fall prevention efforts